3.6. OGC API Features
OGC API Features (OAPIF) is the first implementation of the new generation of OGC protocols. It is described by the OGC API - Features - Part 1: Core document.
The API can be reached on typical installations via http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3
Here is a quick informal summary of the most important differences between the well known WFS protocol and OAPIF:
OAPIF is based on a REST API
OAPIF must follow the OPENAPI specifications
OAPIF supports multiple output formats but it does not dictate any (only GeoJSON and HTML are currently available in QGIS OAPIF) and it uses content negotiation to determine which format is to be served to the client
JSON and HTML are first class citizens in OAPIF
OAPIF is self-documenting (through the
/apiendpoint)OAPIF is fully navigable (through links) and browsable
Important
While the OGC API Features implementation in QGIS can make use of the MAP
parameter to specify the project file, no extra query parameters
are allowed by the OPENAPI specification.
For this reason it is strongly recommended that MAP is not
exposed in the URL and the project file is specified in the
environment by other means (i.e. setting QGIS_PROJECT_FILE
in the environment through a web server rewrite rule).
Note
The API endpoint provides comprehensive documentation of all supported parameters and output formats of your service. The following paragraphs will only describe the most important ones.
3.6.1. Resource representation
The implementation of OGC API Features in QGIS Server currently supports the following resource representation (output) formats:
HTML
JSON
The format that is actually served will depend on content negotiation, but a specific format can be explicitly requested by appending a format specifier to the endpoints.
Supported format specifier extensions are:
.json.html
Additional format specifier aliases may be defined by specific endpoints:
.openapi: alias for.jsonsupported by the API endpoint.geojson: alias for.jsonsupported by the Features and Feature endpoints
3.6.2. Endpoints
The API provides a list of endpoints that the clients can retrieve. The system is designed in such a way that every response provides a set of links to navigate through all the provided resources.
Endpoints points provided by the QGIS implementation are:
Name |
Path |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Landing Page |
|
General information about the service and provides links to all available endpoints |
Conformance |
|
Information about the conformance of the service to the standards |
API |
|
Full description of the endpoints provided by the service and the returned documents structure |
Collections |
|
List of all collections (i.e. ‘vector layers’) provided by the service |
Collection |
|
Information about a collection (name, metadata, extent etc.) |
Features |
|
List of the features provided by the collection |
Feature |
|
Information about a single feature |
Similar to WFS-T (transactional Web Feature Service), it is possible to add, update and delete features (CRUD). The respective requests are described on “/api”.
Landing Page
The main endpoint is the Landing Page. From that page it is possible to navigate to all the available service endpoints. The Landing Page must provide links to
the API definition (path
/apilink relationsservice-descandservice-doc),the Conformance declaration (path
/conformance, link relationconformance), andthe Collections (path
/collections, link relationdata).

Fig. 3.23 Server OAPIF landing page
API Definition
The API Definition is an OPENAPI-compliant description of the
API provided by the service.
In its HTML representation it is a browsable page where all the
endpoints and their response formats are accurately listed and
documented.
The path of this endpoint is /api.
The API definition provides a comprehensive and authoritative documentation of the service, including all supported parameters and returned formats.
Note
This endpoint is analogue to WFS’s GetCapabilities
Collections list
The collections endpoint provides a list of all the collections
available in the service.
Since the service “serves” a single QGIS project the collections are
the vector layers from the current project (if they were published as
WFS in the project properties).
The path of this endpoint is /collections/.

Fig. 3.24 Server OAPIF collections list page
Collection detail
While the collections endpoint does not provide detailed information
about each available collection, that information is available in the
/collections/{collectionId} endpoints.
Typical information includes the extent, a description, CRSs and other
metadata.
The HTML representation also provides a browsable map with the available features.
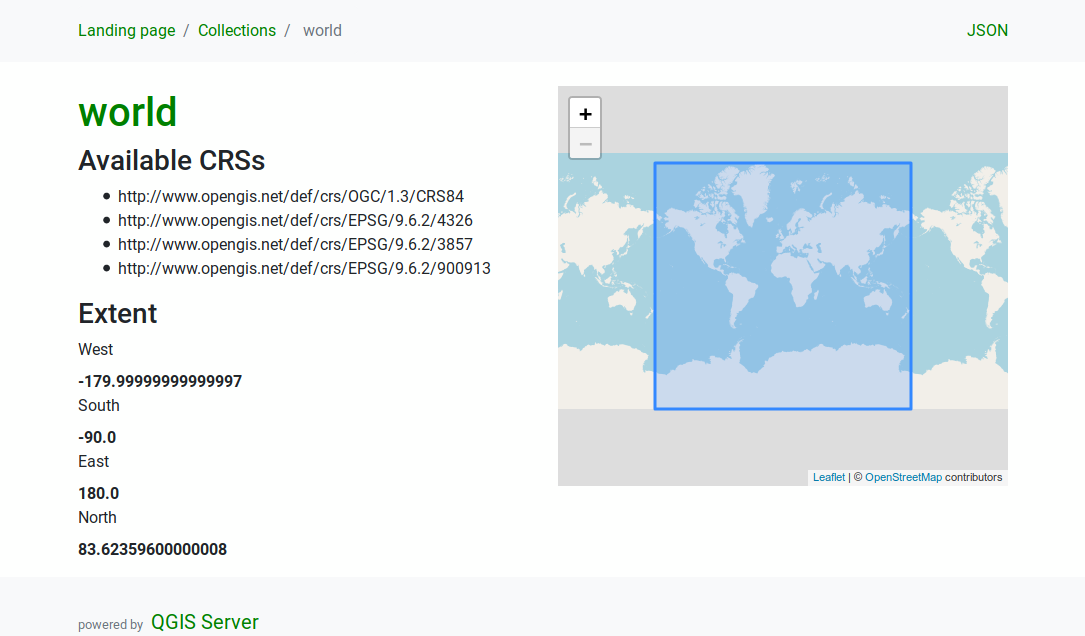
Fig. 3.25 Server OAPIF collection detail page
Features list
This endpoint provides a list of all features in a collection knowing
the collection ID.
The path of this endpoint is /collections/{collectionId}/items.
The HTML representation also provides a browsable map with the available features.
Note
This endpoint is analogue to GetFeature in WFS 1 and WFS 2.
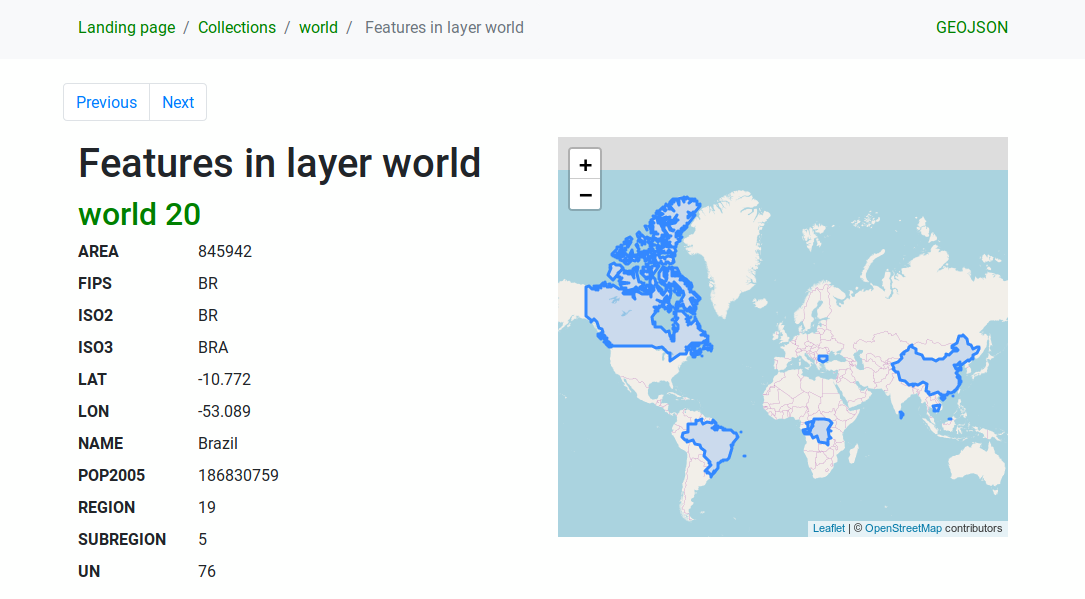
Fig. 3.26 Server OAPIF features list page
Feature detail
This endpoint provides all the available information about a
single feature, including the feature attributes and its geometry.
The path of this endpoint is
/collections/{collectionId}/items/{itemId}.
The HTML representation also provides a browsable map with the feature geometry.
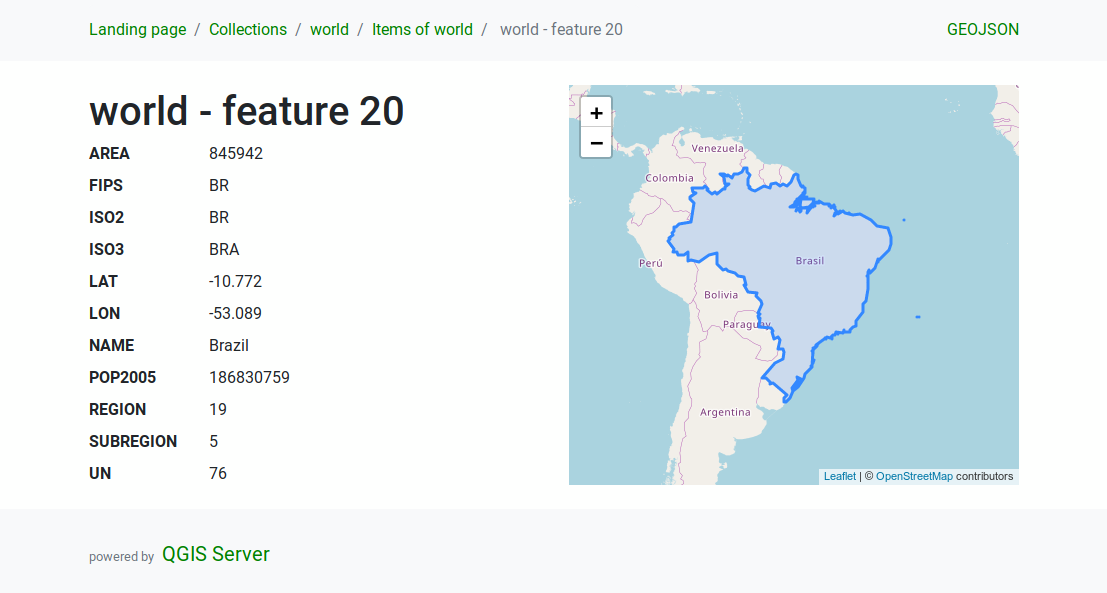
Fig. 3.27 Server OAPIF feature detail page
3.6.3. Pagination
Pagination of a long list of features is implemented in the OGC API
through next and prev links, QGIS server constructs these
links by appending limit and offset as query string
parameters.
URL example:
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?offset=10&limit=10
Note
The maximum acceptable value for limit can be configured with
the QGIS_SERVER_API_WFS3_MAX_LIMIT server configuration setting
(see: Environment variables).
3.6.4. Feature filtering
The features available in a collection can be filtered/searched by specifying one or more filters.
Date and time filter
Collections with date and/or datetime attributes can be filtered by
specifying a datetime argument in the query string.
By default the first date/datetime field is used for filtering.
This behavior can be configured by setting a “Date” or “Time”
dimension in the section of
the layer properties dialog.
The date and time filtering syntax is fully described in the API Definition and also supports ranges (begin and end values are included) in addition to single values.
URL examples:
Returns only the features with date dimension matching 2019-01-01
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?datetime=2019-01-01
Returns only the features with datetime dimension matching
2019-01-01T01:01:01
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?datetime=2019-01-01T01:01:01
Returns only the features with datetime dimension in the range
2019-01-01T01:01:01 - 2019-01-01T12:00:00
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?datetime=2019-01-01T01:01:01/2019-01-01T12:00:00
Bounding box filter
A bounding box spatial filter can be specified with the bbox parameter:
The order of the comma separated elements is:
Lower left corner, WGS 84 longitude
Lower left corner, WGS 84 latitude
Upper right corner, WGS 84 longitude
Upper right corner, WGS 84 latitude
Note
The OGC specifications also allow a 6 item bbox specifier where the third and sixth items are the Z components, this is not yet supported by QGIS server.
URL example:
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?bbox=-180,-90,180,90
If the CRS of the bounding box is not
WGS 84, a different CRS can
be specified by using the optional parameter bbox-crs.
The CRS format identifier must be in the
OGC URI format:
URL example:
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?bbox=913191,5606014,913234,5606029&bbox-crs=http://www.opengis.net/def/crs/EPSG/9.6.2/3857
Attribute filters
Attribute filters can be combined with the bounding box filter and they
are in the general form: <attribute name>=<attribute value>.
Multiple filters can be combined using the AND operator.
URL example:
filters all features where attribute name equals “my value”
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?attribute_one=my%20value
Partial matches are also supported by using a * (“star”) operator:
URL example:
filters all features where attribute name ends with “value”
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?attribute_one=*value
3.6.5. Feature sorting
It is possible to order the result set by field value using the sortby
query parameter.
The results are sorted in ascending order by default.
To sort the results in descending order, a boolean flag (sortdesc) can be set:
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?sortby=name&sortdesc=1
3.6.6. Attribute selection
The feature attributes returned by a Features list
call can be limited by adding a comma separated list of attribute names
in the optional properties query string argument.
URL example:
returns only the name attribute
http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/collection_one/items.json?properties=name
3.6.7. Customize the HTML pages
The HTML representation uses a set of HTML templates to generate the
response.
The template is parsed by a template engine called
inja.
The templates can be customized by overriding them (see:
Template overrides).
The template has access to the same data that are available to the
JSON representation and a few additional functions are available to
the template:
Custom template functions
path_append( path ): appends a directory path to the current urlpath_chomp( n ): removes the specified number “n” of directory components from the current url pathjson_dump( ): prints the JSON data passed to the templatestatic( path ): returns the full URL to the specified static path. For example: “static( “/style/black.css” )” with a root path “http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3” will return “http://localhost/qgisserver/wfs3/static/style/black.css”.links_filter( links, key, value ): Returns filtered links from a link listcontent_type_name( content_type ): Returns a short name from a content type, for example “text/html” will return “HTML”nl2br( text ): Returns the input text with all newlines replaced by “<br>” tagsstarts_with( string, prefix ): returns true if a string begins with the provided string prefix, false otherwise
Template overrides
Templates and static assets are stored in subdirectories of the QGIS
server default API resource directory
(/usr/share/qgis/resources/server/api/ on a Linux system), the
base directory can be customized by changing the environment variable
QGIS_SERVER_API_RESOURCES_DIRECTORY.
A typical Linux installation will have the following directory tree:
/usr/share/qgis/resources/server/api/
└── ogc
├── schema.json
├── static
│ ├── jsonFormatter.min.css
│ ├── jsonFormatter.min.js
│ └── style.css
└── templates
└── wfs3
├── describeCollection.html
├── describeCollections.html
├── footer.html
├── getApiDescription.html
├── getFeature.html
├── getFeatures.html
├── getLandingPage.html
├── getRequirementClasses.html
├── header.html
├── leaflet_map.html
└── links.html
To override the templates you can copy the whole tree to another location
and point QGIS_SERVER_API_RESOURCES_DIRECTORY to the new location.